Group1
数组中重复的数字
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/14/
- 先遍历数组,若有超过区间 [0, n-1] 的数值,就直接返回 -1
- 再遍历一次数组,如果当前位置的数值与下标不一样。
- 且数值对应的那个下标与当前位置的值不同,就交换它们的位置。
- 若一样,则说明找到了重复元素了
1 | class Solution { |
不修改数组找出重复的数字
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/15/
- 抽屉原理:将 n+1 个苹果放进 n 个抽屉,必然会有两个苹果在一个抽屉的情况
分治(二分)的思想,根据数值大小(注意不是下标)将整个区间一分为二。
- 因为数值范围是 [1, n],所以假设总共有 n 个坑位。也就是说
- 又因为共有 n+1 个数,所以,起码会有一边数的个数会大于坑位的个数。
- 不断找到这个区间并再次划分左右,直到区间内只存在一个数,这个数就一定是重复数字
1 | class Solution { |
二维数组中的查找
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/16/
这里可以看出,第 0 行的最后一列是该行最大,该列最小。所以从矩阵的右上角开始遍历。
- 正好等于目标值直接返回 true
- 大于目标值,说明目标一定在更小的列
- 小于目标值,则一定在更大的行
1 | class Solution { |
替换空格
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/17/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ti-huan-kong-ge-lcof
- 很简单,开一个新字符串,再遍历源字符串,遇到空格就加
%20,否则就加原字符
1 | class Solution { |
从尾到头打印链表
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/18/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cong-wei-dao-tou-da-yin-lian-biao-lcof/
- 创建数组,遍历链表,依次将值压入数组
- 逆序返回
1 | /** |
重建二叉树
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/23/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/zhong-jian-er-cha-shu-lcof/
- 先用哈希表记录中序遍历每个值的位置,以便于后面找根节点位置
- 搜索过程中
- 先判断序列长度,如果序列为空就返回空指针
- 然后前序遍历的左边界值
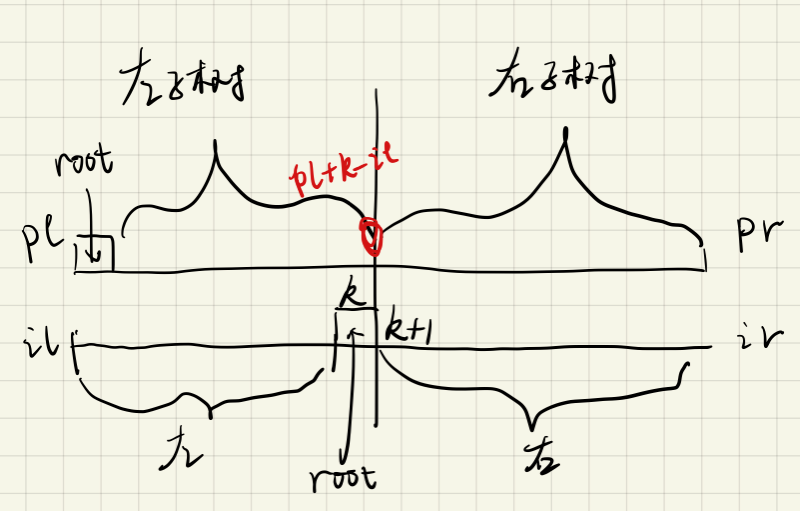
preorder[pl]一定是根节点,根据这个值在哈希表中找到中序遍历的位置 - 分别递归求出下一个左子树及右子树,然后插到 root 上就可以恢复二叉树了
其中 dfs 的几个参数前两个分别为前序遍历的左右边界,后两个分别是中序遍历的左右边界。求下一个左右子树时,区间范围的确定可以参考下图
1 | /** |
二叉树的下一个节点
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/31/
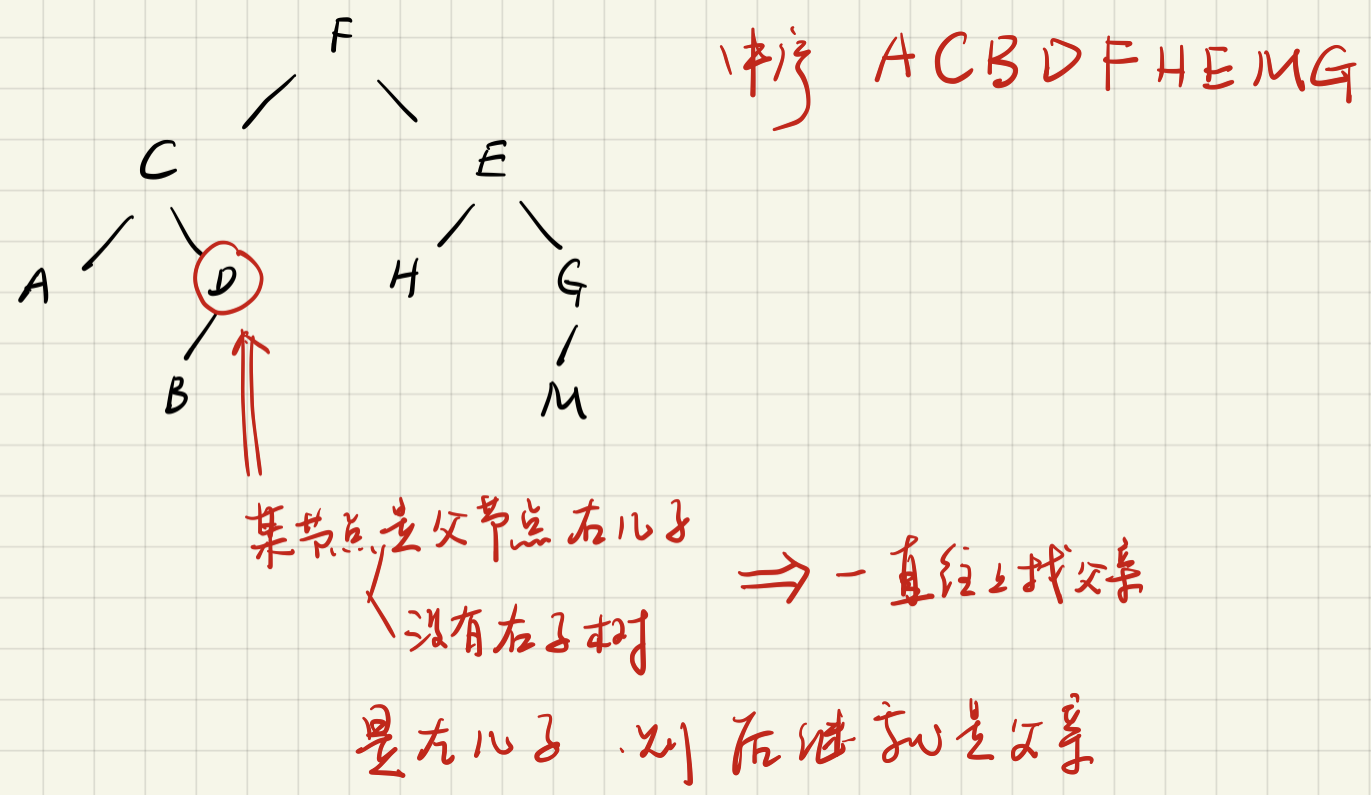
- 情况一:如果某节点有右子树,那么右子树的最左侧节点就是后继
- 情况二:没有右子树。
- 该节点是其父亲的右儿子:一直往上找父亲,直到父亲为 NULL
- 该节点是父亲的左儿子:其父亲就是后继(因为中序)
1 | /** |
Group2
机器人的运动范围
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/22/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ji-qi-ren-de-yun-dong-fan-wei-lcof/
- BFS
- 将
{0,0}压入队列,如果坐标各位之和满足要求,且没有被遍历过则结果 res 加 1 - 后面的 for 循环用于对坐标的移动,因为从最左上角开始,所以横纵坐标只需要朝着右下移动即可。所以 dx 和 dy 只需要两个维度,遍历到的坐标都压入队列中。
- 将
1 | class Solution { |
剪绳子
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/24/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jian-sheng-zi-lcof/
我们假设 $N>0$,可以将 $N$ 分隔成若干份,有 $N=n_1+n_2+n_3+…+n_k$
假设存在其中一个数值 $n_i>=5$,但是如果我们从这个数值中分出一个 3 来,再构造乘积,其结果一定是大于等于 $n_i$ 的,也即有 $3\times(n_i-3)\geq n_i$。证明如下:
由上式可得 $3\times n_i-9\geq n_i$
则 $n_i\geq 4.5$ 这是满足假设条件的,所以 $3\times(n_i-3)\geq n_i$ 一定成立,因此分割后的值一定不会存在大于等于 5 的情况
假设存在一个数值等于 4,而 4 可以分为 $2\times2$,没有影响,所以也可以不存在 4
- 假设存在三个 2,也即 $2\times2\times2$,但是这个被分割的值原本为 6,可以分成 $3\times3$ 显然比分成三个 2 要大。
所以,综上,数值最终由 2 和 3 组成,2 的个数不超过 3 个。如果 2 的个数为 2,实际上就对应假设二,这个时候将结果乘以 4 并将值减去 4,就排除了这种情况,剩下只有一个 2 和若干 3 的情况。
1 | class Solution { |
二进制中 1 的个数
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/25/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/er-jin-zhi-zhong-1de-ge-shu-lcof/
这里需要对无符号数进行移位,否则,右移会补符号位。
1 | class Solution { |
数值的整数次方
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/26/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-zhi-de-zheng-shu-ci-fang-lcof/
常规做法(超时)
1 | class Solution { |
快速幂 参考
思想是二分。推导过程如下:
$x^{n}=x^{\frac{n}{2}}\times x^{\frac{n}{2}}=(x^2)^{\frac{n}{2}}$
- 当 $n$ 为偶数:$x^n=(x^2)^{n//2}$ (
//为整除) - 当 $n$ 为奇数:$x^n=x\times (x^2)^{n//2}$ 会多出一个 $x$
- 当 $n$ 为偶数:$x^n=(x^2)^{n//2}$ (
循环执行 $x=x^2$ 的赋值操作,将幂从 $n$ 将为 $\frac{n}{2}$ 直至 0
1 | class Solution { |
删除链表结点
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shan-chu-lian-biao-de-jie-dian-lcof/
如果下一节点不为空,当下一节点值满足期望时,将下一节点的下一节点的指针给到当前节点的下一节点即可。
1 | /** |
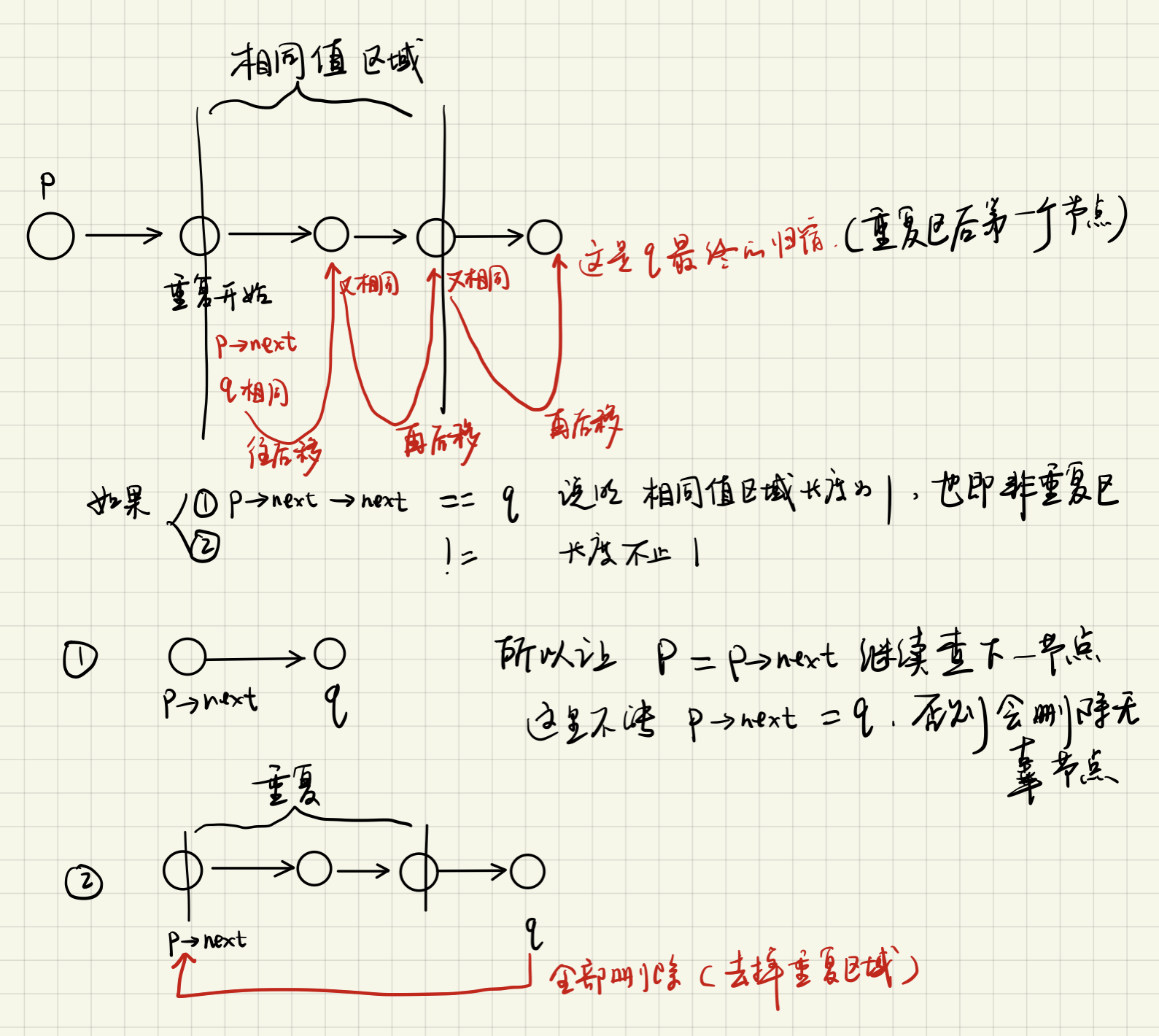
删除链表中重复的节点
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/27/
1 | /** |
正则表达式匹配
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/28/
f[i][j]表示p从j开始到结尾,是否能匹配s从i开始到结尾
- p[j]是正常字符,
f[i][j]=s[i]==p[j]&&f[i+1][j+1] - p[j]是”.”,
f[i][j]=f[i+1][j+1] - p[j+1]是”“,
s[i]==p[j]&&f[i][j]=f[i+1][j]||f[i][j+2](类似 `b`这种情况)